Fundamental contributions of the Babylonians in terms of technique, science, medicine, astronomy and law.
Technology in antiquity:Refers to advances in the development of tools and utensils for practical or decorative use, as well as the ability to use products of good quality for better results and production on a larger scale.
Babylonians were very skills in different techniques that contribute to make great advances in their civilization. Among those advances are:
– The prevention and contagion of diseases with the application of personal hygiene measures that included frequent ablutions, hand washing, water boiling and elaboration with this one of both medicinal and common use beverages. They detailed on the tablets the symbols and signs that correspond to the different diseases known to them and how to treat them effectively.
– Creation and implementation of the first criminal code of laws to govern the behavior of people.
– Creation of religious cults that propagated with modified versions towards other cultures in antiquity.
– They were able to obtain alloys of metals with which they produced tools, weapons and elements of decorative and utilitarian character like metal sculptures, jewels, metal vessels, shields, swords, bracelets etc.
– Advanced knowledge in the use of irrigation for agriculture, recycling of land and crops.
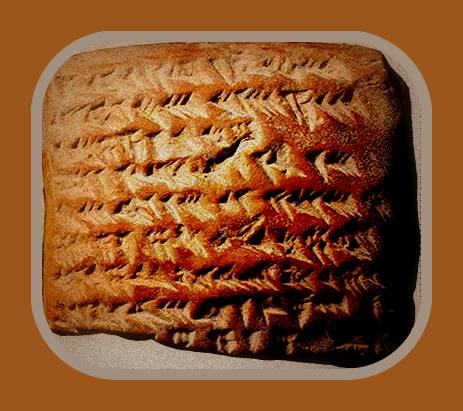
– The use of cuneiform writing on cylinders and slabs of baked clay technique inherited from the Sumerians, has provided valuable information with which it could document aspects of its history, traditions and culture.
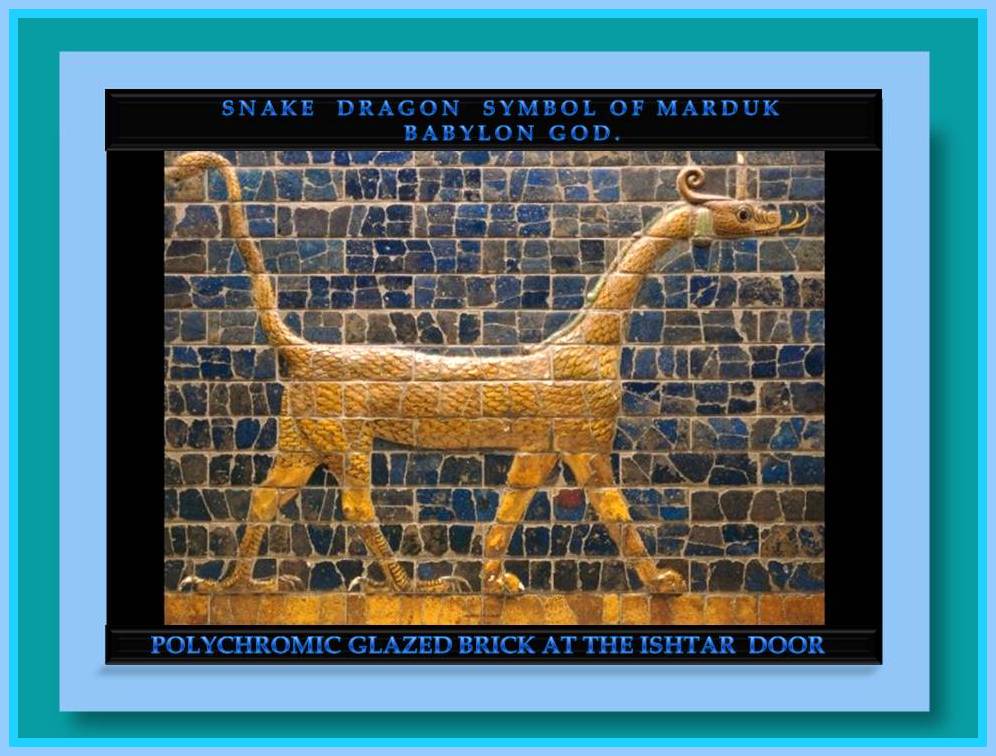
– Amazing technique for the elaboration of vitrified bricks used for the decoration of palaces and temples.
– Advanced mathematical and astronomical knowledge about the constellations, distance from the earth to the sun, the solstices and equinoxes, which the earth’s orbit was elliptical, placed the sun as the center of the galaxy, the number of planets in our galaxy among others.
– The creation of the wheel in Sumeria and extensive use of it in all Mesopotamia.
The Babylonians and medicine.
The Babylonians achieved important results in the treatment of diseases from natural organic compounds such as honey and medicinal plants. The prevention and contagion of diseases with the application of measures of personal hygiene that included frequent ablutions, washing of the hands, boiling of water and elaboration with this one of both medicinal drinks and those with common use.
The Babylonian physicians were able to operate their patients fairly effectively and were punished if their patients died as stipulated in their code of laws.
In Mesopotamia all as it was in Babylon were introduced over time concepts of disease diagnosis and prognosis of patients’ health status, as well as the study of possible complications, based on previous experiences recorded on their ceramic tablets in cuneiform script.
These tablets; that came to form a kind of compilation or book on the subject reflected in detail, descriptions containing symbols and signs that corresponded to the different diseases, known by them and how to treat them effectively.
The cleaning of the city was seen by the Mesopotamian cultures as an important element for the prevention of diseases. From where they obtained that knowledge? That still remains a mystery, especially if it’s consider that we are talking about human conglomerates that conformed civilizations in the Neolithic period. Their advances are equivalent to thousand of years of observation, so it is remarkable and curious they have
all this knowledge suddenly from the beginning of their civilization. This opens more questions that need to be investigate seriously.
Works with metal in Babylon and Mesopotamia.

They were able to obtain metal alloys with which they produced tools, weapons as well as decorative and utilitarian elements such as metal sculptures.
Techniques like “The granulation”, of fine appearance and great variety, as well as the system consistent of embossing the metal; with exquisite mastery in the results. This objects were widely used in jewelry, decoration of arms, shields to use in war, metallic vases etc.
They did not make these objects for their own personal consumption only, but were marketed else where too, having a wide demand for their quality, even in geographically remote areas. Their technique of applying beads of Chalcedony was very popular at that time as well as their beautiful works in the applications of Lapis lazuli Technique.
Babylonian system of laws.
The city of Babylon reaches its maximum splendor with the figure of king Hammurabi, more important of the first dynasty of Babylon, that reigned between the years 1792 and 1750 A.C. He cemented and forged the foundations of the Babylonian Empire.
The code of laws of Hammurabi, is the first legislation that is known in history, has an amazing property and is its ability to be understood, its wisdom and understanding of human behavior. More can be found in the article about Hammurabi and the code of Laws.

The glazed bricks of Babylon.
Among the techniques developed by the Babylonians is the elaboration of vitrified bricks used for the decoration of palaces and temples. It highlights the decoration of the entrance of the city known as “The Gate of Istar” in which many vitrified bricks colored with intense shades of blue and other colors give us representations of animals that were supposed to protect the entrance to the city .
This technique imitated by other cultures has unfortunately disappeared and despite attempts to reproduce it, at present the attempts have been unsuccessful. It is a mystery how they managed to produce these vitrified bricks in substantial quantities. The pigments used from nature’s own materials were diluted in exact, millimeter quantities and reproducing this on a large scale required a knowledge of chemistry and properties of the natural compounds that is truly a mystery how they manages to achieved, or how they obtain that knowledge, that even today has not been able to be reproduced.

Advanced knowledge of astronomy and creation of astrology in Mesopotamia.
One of the great mysteries that this culture presents to us is, how it was possible for them, the Sumerians and the Assyrians to know advanced elements of astronomy as if they could have contemplated the cosmos from an external perspective to the earth and not a simple contemplation of the stars from the surface of the planet and obtaining that knowledge during only the short time that this culture arose, later developed and was extinguished.
They knew the number of planets of the solar system.In a relief it is shown a representation of the solar system with the planets revolving around the sun. They have specific mathematical and astronomical knowledge about the constellations, distance from the earth to the sun, the solstices and equinoxes, that the earth’s orbit was elliptical, they knew how to calculate the movements of the sun, moon, stars and planets.
They could calculate the occurrence of eclipses of sun and moon. They new about the Precession of the equinoxes and solstices. This information came to be re-discovered by science thousand of years after the flowering of this cultures in Mesopotamia.They placed the sun as the center of the galaxy around which the planets revolved.

The invention and utilization of the wheel.
The discovery of the wheel in Sumer around 3500 (BC) in the Mesopotamian region was one of the most important technological advances in the history of man. The Babylonians welcomed this invention and developed it even more in the sense of the multiple applications for which they used the wheel. It is almost impossible to realize a mechanism of movement nowadays that does not involve the use of the wheel.
They were use in militarist campaigns constructing the war wagons, in agriculture to propel water to the place needed, to move mechanisms for different use.
Advanced knowledge on the use of irrigation for agriculture, recycling of land and crops, allowed them not only to settle in these areas that had limitations with conditions not suitable for agriculture, but to prosper in a way that was possible to increase population and sustaining it through the infrastructure they developed, making it one of the most important empires of the time whose technical and scientific advances were assimilated by other cultures as well.
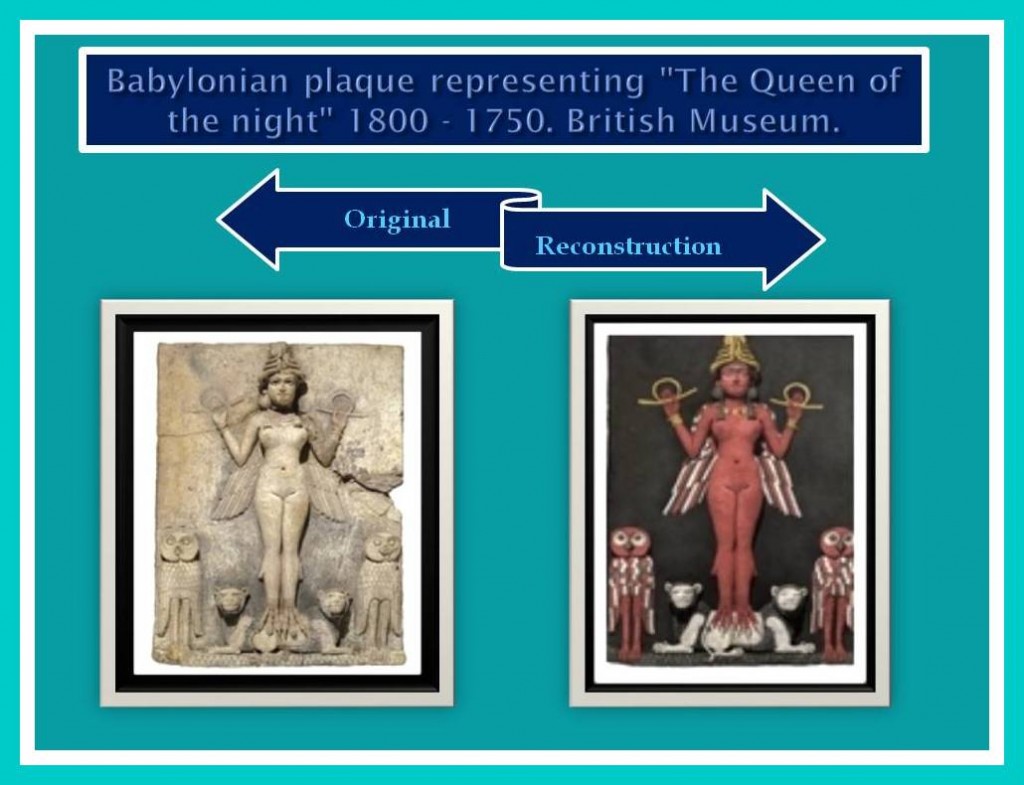
Babylonian rituals, worship and temples.
Human beings at that time worshiped a deity or heroic figure; and those adoration and rituals were present in Babylon and contributed to create and to foment the cults propagating them by the world. Those cults were based on stories that curiously had points of contact with the stories and cult of other cultures in the rest of the planet. Many of these stories coincide with even bible passages, and histories or the so called mythologies such as Greek and Romans.
Buildings and temples were done based on knowledge of mathematical measures and physical principles which nowadays seem normal to know, but the big question is how the Babylonians and Mesopotamian cultures knew it 5000 years ago?
With the translation of the tablets written in cuneiform, progressively new elements are seeing the light, that contribute a little more to know who were the Babylonians and the cultures with which they were related by invasions or simple commercial relations. More about Babylonian mythology can be found in an article expanding this information in the blog.