Mesolithic (Middle Stone age) art
10.000-8000 a.C
Also known as “Middle Stone age”, the Mesolithic period covers a brief time span of about 2,000 years. It served as an important bridge between the upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic age, the art of this period had no relevant artistic connotations in the form of representation in comparison with predecessor times.
The art of the later Neolithic period varies exponentially, as well as being better preserved and offer us thousands of art examples rather than a “handful” as in the case of the Mesolithic. Let’s briefly cover the artistic Mesolithic events because, after all, it is different from any other time period in the prehistoric man history. Geography and climate had changed and people gradually had adapted, assisted by a more temperate climate and various edible plants were there on hand to aid in survival.
Given that human beings do not have to live in caves or follow herds any more, this era saw the beginning of settled and agricultural communities. The invention of the bow and the arrow helped to provide more food from the hunting of animals and the development of ceramics for food storage; It was definitely a step forward.
The domestication of animals – for food in the development of a more pastoral lifestyle, or in the case of dogs, for help in the hunt for food was another element of prosperity in their live that allowed better conditions for the settlement.
The pottery, although it was largely produced was intended to be utilitarian only to contain water or grain, not necessarily for embellishment or visual pleasure. The portable statuary of the Upper Paleolithic was largely absent during the Mesolithic era. This is probably the reason why people settled and did not require an art with small objects or portable with which to travel. The Highlights at this time is the carvings of obsidian and other objects with jagged edges.
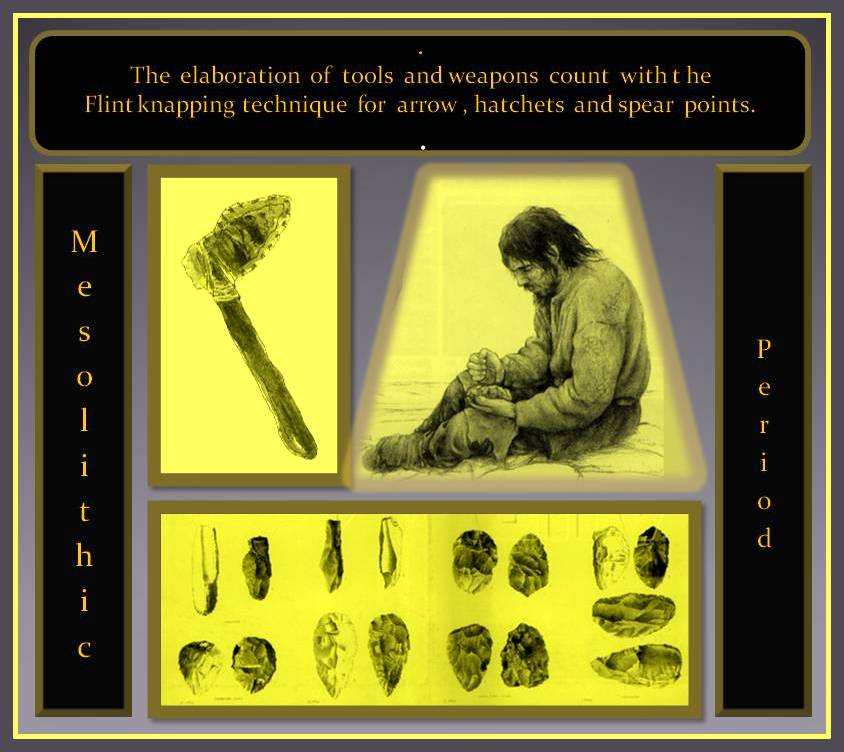
The elaboration of tools and weapons count with the Flint knapping technique for arrow and spear points used in large spear like sticks and also for hand use type, been done profusely. Other tools such as scrapers for cleaning hides and knives were also made from flint.
The most interesting Mesolithic art as we know of consists of paintings similar to the cave paintings from the Paleolithic era, these move abroad towards cliffs or “walls” of natural vertical rock , often semi-protected by outcrops or overhangs of natural rocks. Although these cave paintings have been found in places ranging from the extreme north of Europe to South Africa, as well as in other parts of the world, the largest concentration of them exists in the East of Spain.
Main features of the Mesolithic art
– The paintings of this time change in regards to the topics where there are human groups participating in hunts or rituals.
– Human beings shown in the cave painting are highly stylized, as glorified stick figures. These human beings look more like images pictographs, and some historians pose representing the primitive beginnings of writing (e.g.: hieroglyphs).
– Very often the groupings of figures are painted in repetitive patterns, resulting in a good sense of rhythm, even if you are not sure of the action in which they are involved.