Gothic Art Architecture
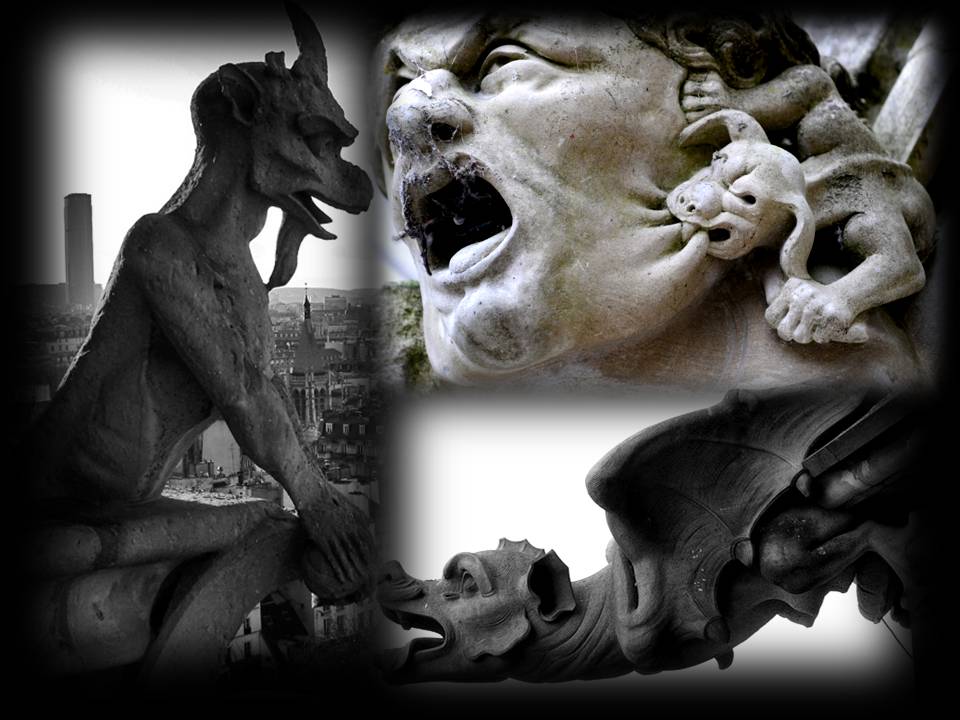
The architecture was the first manifestation of artistic development in Gothic art and it has a wealth of forms and accentuated ornamental variety that intensifies gradually coming to cover the external walls of these buildings with beautiful decorations. Sculptures with religious themes, vegetal and geometric motives join gargoyles, canopies and beasts like figures of fearful aspect in its pinnacles and flying buttresses. Sculptures and reliefs that are placed by thousands in the outer part of the cathedrals look more realistic, moving away from the symbolism of the Romanesque era.
The Gothic Cathedral is the main building during this long period in the middle ages, representative of the ideals of the new bourgeoisie and its most refined tastes. This architecture is monumental, is constantly seeking to extend its structures as high as possible, thanks to new techniques to lighten the walls allowing out magnificent upward constructions carried out with voluntary labor and the contribution of craftsmen guilds.
This search for closeness to God and his heavenly kingdom justify the unbridled search for elevation for which displayed a remarkable number of innovative construction techniques and masterful display of engineering and mathematical knowledge. Regions compete for having the highest Cathedral and this leads to a constant challenge in the search for technical solutions that make possible such audacity.

New religious tendency make light a leading element, for them light represents God and the more iluminated were those enclosures more effective communication with God, therefore the spatial conception of these cathedrals focuses on the effective use of the light coming from the outside. Also pay attention to the architectural space designed to properly locate luminaries, chandeliers and any other element of lighting where daylight does not get there or during hours when it was not available.
In the large openings at the front of Cathedral were placed an enormous amount of stained glass containing historical narrations about the martyrs of faith with colorful decorations through were plenty of natural light filled the spaces. Among these amazing decorations are beautiful circular rosettes also in glass with both religious scenes as with ornamental forms placed radial from a prominent center usually on the main façade and the arms of the transept (the transversal gathering large room that crosses the big salon in the churches).
In the Gothic style the capitals lose its importance within the framework of the building instead of sum importance are the Baquetoneado a type of rounded molding that looks like a stem of a plant that is vertically row-shaped one with the other forming the support column. Although the Baquetoneado process do not reinforce the column as such properly from the structural point of view, if helps give visual unity to the space of the Gothic building and mark the lines of force that guide the displacement of the tensions of the dome to the ground. In these columns is where rest the nerves of the vaulted naves. These columns with ramrods are known also by fasciculate pillar having different decorative variations.
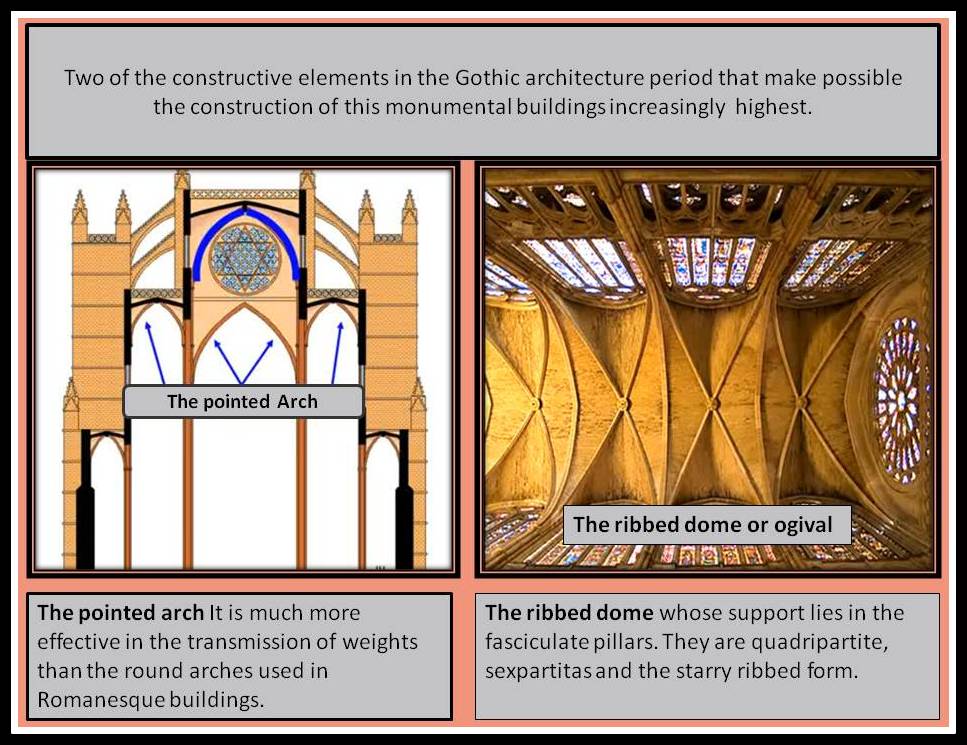
Main construction elements of Gothic art:
–The pointed arch It is much more effective in the transmission of weights than the round arches used in Romanesque buildings.
–The ribbed dome or ogival whose support lies in the fasciculate pillars. They endure only vertical forces. The vaults are evolving from the quadripartite or ribbed, the sexpartitas, (six nerves) and the starry ribbed form.
–The flying buttresses: Are elements of lateral push that complement the resistance of the structural pressures allowing a lighter wall and build higher.
–The buttresses: Structural support element attached on the outside of the walls to lighten the weight of these ones.
Topics and main motives used in buildings decoration on Gothic architecture.
1 –Of tracery. (Ornamental decorative lines of branched that support the work in windows) Among them are:
(a)Geometric motives.
(b) Clovers and flamboyant designs.
2 –The naturalist topics that include:
(a)Designs with vegetable motifs.
(b)Which represent animals and mythical beasts.
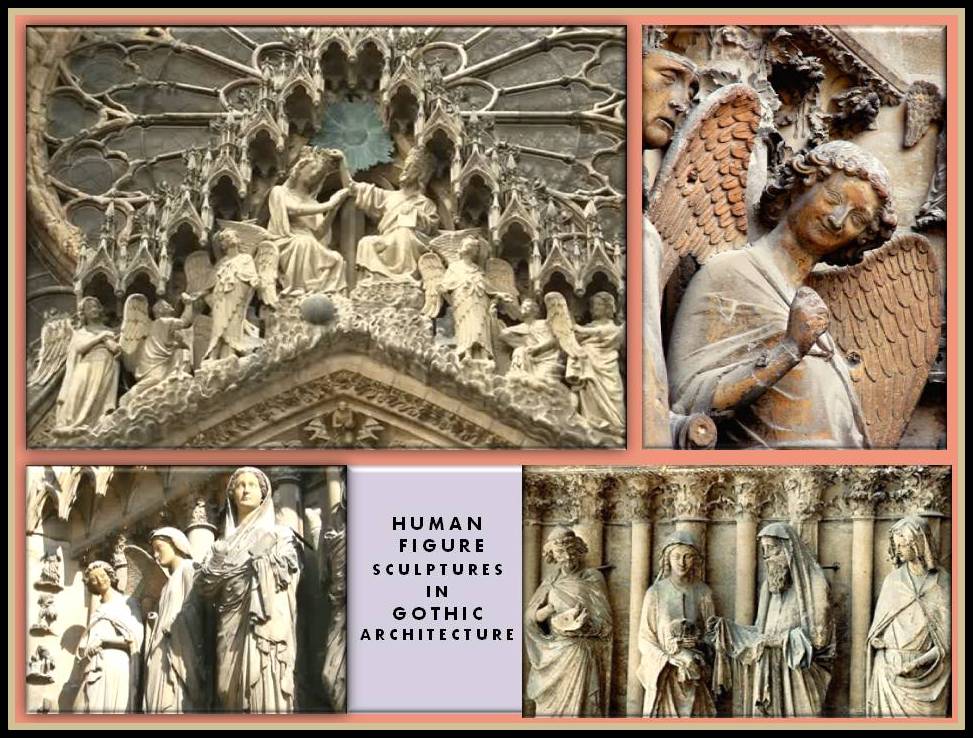
(c)Representations of the human figure.
In these lavish Gothic cathedrals altarpieces takes place an evolution in the front of the altar dominated mostly for decorations relating to the last supper, sacred stories to the martyrdom of Jesus on the cross and the descent from the same. It occur a widening proliferation of sculptures to decorate the architectural spaces, both indoor and outdoor. Sculptures are placed in the flying buttresses and prominent pointed structures, some looking beast like forms. Outstanding carved works in choirs have a profuse decorative style done with masterful skill and quality.
Main changes in Gothic decorative elements and the sculptures locations.
-The eardrum in this new style is pointed and they are divided into strips or bands.
-The archivolts are longitudinally as opposed to the previous Romanesque style in which were vertically.
-The jambs are also sculptures with canopies of Gothic tracery.
-In the transept are located sculptures under the canopy.
-The Gables (a triangular ornamental wall, built on an arch with very acute form) underlined the verticality of the set.
The plant and the uprising of the Gothic buildings:
-The plants of Latin cross are maintained on these monumental cathedrals with three or five Naves with the transept highlighted.
-They have ambulatory with to hall and radial chapels.
-Dome.
-Altar.
-Transept.
-In the uprising are made present galleries and clerestories placing on them the clerestory (which is the level where the large windows are). This is the top point on the side walls and gradually occupying more and more space over time as they are becoming higher buildings.
-The facades have capitals that are large towers topped with needles. (These capitals resemble lace due to the draught that is abundant in stone decoration). They emphasize the height of the building on the outside.
In the Gothic period sculptures are gradually released from its architectural framework and changes occur in the gestural treatment and in the representation of the characters that are symbolized. In the eardrums of the facades are reliefs and sculptures with the theme of Christ risen and triumphant, the Marian theme and scenes from the old and New Testament.
During the stage of the so-called Gothic Classic, through the Court of Fernando III French influence is reflected in the cathedrals of Burgos, Toledo and Leon. But it should be noted that the Spanish cathedrals were not parochial copies of the French models, and in them can be perceived architectural and decorative features of the Hispanic culture, as they were Muslin elements from the time of Arab domination.
In the 14th century the greatest architectural progress occurred in Catalonia and Levant, with examples like the cathedrals of Barcelona, Palma de Mallorca and Gerona. In this area it is adapted to the propositions and foundations of the South of France, by what has been called Mediterranean Gothic.
The unique features of English style include structures with extreme length and height that incorporated very elaborate desings but really beautiful . Additionally, those buildings moved away from large, bulky structures to more elegant, thin and refined works. Ornamentation and decoration both internally and externally utilized carvings and detailed capitals. The “Perpendicular Style” is unique to England and cannot be found in other European countries. It developed after the “Decorated Style” and marked the last era of Gothic Architecture in England. All this elements are very important because they made possible the way to Renaissance style in the 16th and 17th century.
In German Cathedrals the moldings used were simple and basic no so elaborated like they were made for example in England. The most internal distinctive feature of German Gothic design was the great height of the triforium, a shallow gallery of arches within the thickness of inner wall, which stands above the nave. Although buildings in Germany possess many structures pretty much standars or specific to Gothic Architecture, quite amount of then possess a distinct national character that is not found in other European countries.
German designers experimented with geometrical figures and lines, which mostly translated into elaborate tracery for windows and paneling.
Civilian Buildings in Gothic architecture
Although preeminent the religious architecture; civilian buildings have also become important in Gothic period as for example private residences and the palatial type. Improvements in the quality of life are introduced in these buildings which although not characterized by the pursuit of height as in cathedrals, if stand by the richness, comfort and abundant decoration on the outside in many of them. Corridors with sequence of ogival arches between the thin columns and decorated capitals are placed both outside and inside the buildings.
These edifices of a civil nature and the one dedicated to the Administration and political centers reflect plant and Freehand designs typical of the architecture in the Gothic art but also respond to local regions specifications where they were built so; a great architectural variety it is observed across Europe. As example are those carried out for housing of the bourgeoisie and the upper class as well as major universities where now is studying also the culture and art outside of the churches.
In Italy they acquire huge practical importance as a meeting place congregation and business centre, adapting to urban conditions and away from the militarization of medieval castles. Among these buildings in Italy are the communal Palace of Siena and the Vecchio palace of the Signoria in Florence. Highly for its beauty and local adaptability the ones located in Venice are very important as well.
In Spain the civil buildings during the greater part of the Gothic and the high Gothic remain faithful to the French models but develop decorative elements of Arab influence, (Mudéjar) which led to the formation of local stylistic variants . Significantly in Valencia are The Silk Exchange, the Palace of Generalitat in Valencia and the Palace of the Borja family. The Civil Gothic building in Catalonia shows its splendor in the Palace Mayor Real of Barcelona, the Palace of the Generalitat of Catalonia and the Santa Cruz of Barcelona Hospital.
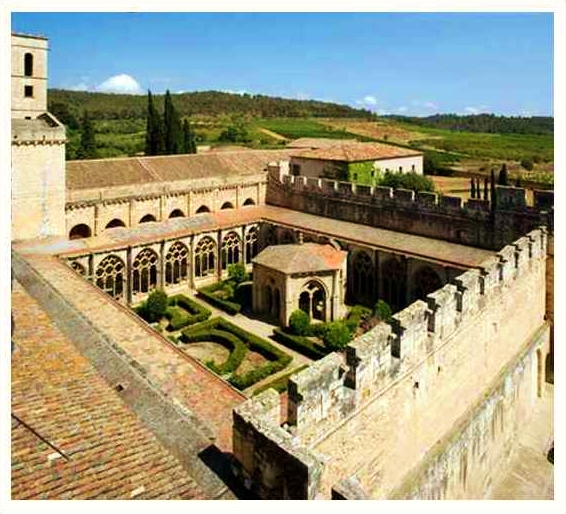
In the Gothic period not all the cathedrals made in this style were decorated with rich elements because this factor of monumental construction seeking high was not present in order consagrated to poverty. Therefore are differences in the level of decorative elements among the cathedrals of the order of Cluny and the Cistercian monasteries since the latter reflected an austere art corresponding to the ideals that advocates the Cistercian Order for instance:
The CISTERCIAN Orders simplifies some elements
- Only have two floors
- The stained glass windows are not colored.
- They have no triforium.
- The capitals are cubic and without decoration.
- The transept and the apse are not deep.
- the utilitarian dependencies are separated from the main building.