Ancient Sumerian culture
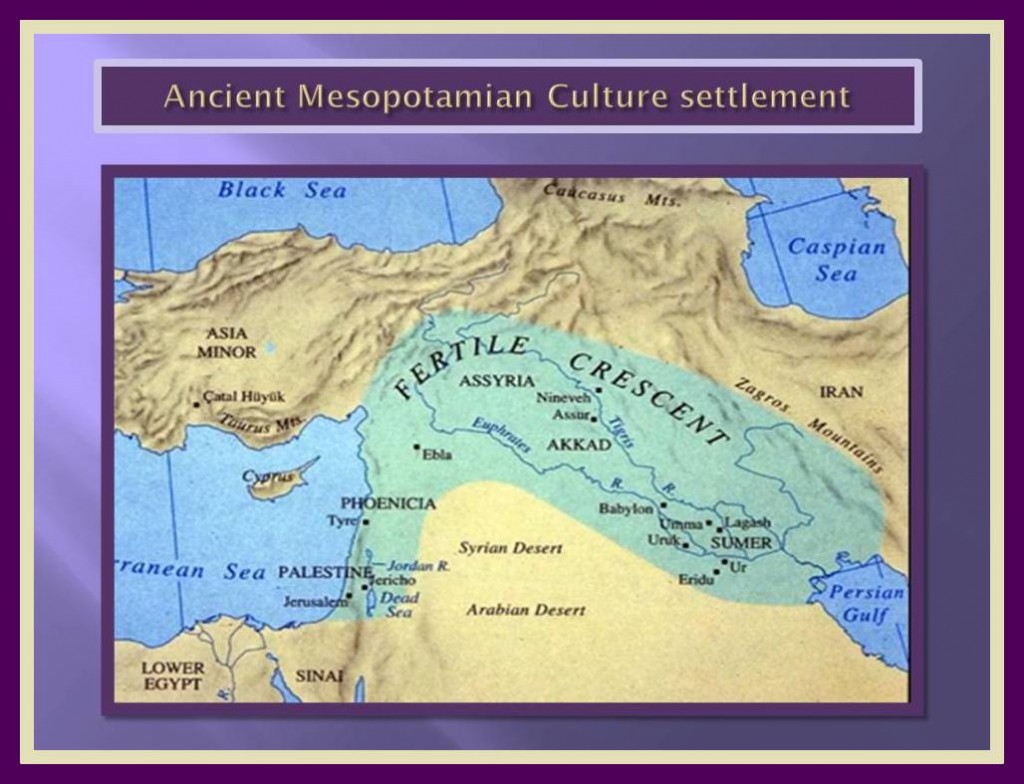
History traditionally established the beginning of civilizations; either in Egypt first or in the fertile valleys of the Euphrates and the Tigris latter, were indeed took place one of the earliest forms of coexistence which could be considered civilized forms of social organization, although they were not the first. This region is referred to as “Mesopotamia” which means between two rivers. From the Neolithic period were uncovered recently some man made stone structures, probably ceremonials, located no far from where the two rivers run fertilizing this land.
This structures in Gobekli Tepe had been dated from around 12 ,000 to 10,000; although the civilization who build the ceremony structures, most has been already developed much early. Some human settlements were established in the immediate zone to where the ceremony circles were made, although they most have to walk considerable distances to get to the ceremonial place nevertheless. This recently uncovered settlements, are subject of intense studies to determine this people level of evolution and complexity of their social gathering.
The same depp studies are carry up to other human settlements in different places of the planet: like for example Mohenjo Daro and Dholavira in India or in other places like China, because they are showing rest of developed ancient civilizations as well, olders than the ones formed in mesopotamia and Egypt.
The circular stone pillars in Gobekli Tepe reveal that Stone Age man had a surprisingly high level of artistic sophistication and that is proof of an already extremely complex specialization that mark the beginning of a more multifaceted society. The stone circular complex date 2,000 years before man settled permanently to farm.
This important recent discovery had radically change our understanding of the birth of civilization. The new knowledge reveals that hunter-gatherer societies in the Neolithic Period were more organized than we previously think. Historians and archeologist had become to the conclusion that the planning and organization of this structures in the valley of Gobekli Tepe show organized societies of man even that they are not completed settled, because they still are hunters and gathering people who nevertheless initiate some form of primitive storages rooms for food, to distribute to all participants in the ceremony monument construction. It seems that for the Gobekli Tepe men’s religion lead them to form group and meet resources and efforts to construct such big ceremonies carved stone figures, leaving their mark in man made artistic monuments starting 10,000 years ago.
The agriculture enable nevertheless a development that transformed what is was until then a society forced to ride a wandering or nomadic life into civilized societies with sedentary features, factor that provide the possibility for improving the artistic manifestations, initiated with the adoration purpose first and then extended to other expression like decoration with the intention to narrate other important aspects of their daily life.
SUMERIA
Many years later others people settled in the Mesopotamia region and more complex civilizations were found, starting by the Sumerian culture and following by Babylonians and Assyrians.
Sumer – Ubaid culture
We will now focus in the civilization that settled in Sumer in the southwest region of Mesopotamia, which corresponds to the present-day IRAQ. They emerged and subsequent flourishing between the period that corresponds to the late copper age and the beginnings of the Bronze Age. This civilization called “UBAID” can be considered the first who established and becomes a predominant force in this region after coming from northern of Mesopotamia.
Their settlement and development can be positioned between the 3600 and 4000 B.C. Although these first settlers of Sumer did not speak the Sumerian language.
The cities of Sumer were the first to develop a system of agriculture involving work carried out throughout the entire year, with its stages of planting, cultivation and harvesting. They installed an irrigation system that allowed them to gather these crops with considerable success and attended by a force of labored farmers specialized in it.
The invention of the wheel and a better technique in the production of metals allowed this culture with important advances in the field of agriculture.

In addition to agriculture, the Ubaid culture developed a commercial exchange, established certain industries such as weaving and also worked the skins, the masonry, metallurgy and ceramics.
The unique works of art of the Ubaid period that are known to us are their clay figurines made by hand, almost always naked female figures, they are carefully made with detail in the finish; the bodies show to be subject to certain conventions, such as the marked angularity of the shoulders.Figures are quite realistic but static; showing a geometric simplification in shapes and large eyes.
These minor arts are characteristic of the Ubaid culture; but it was in the architecture were Ubaid made an immediate and most lasting contribution.
In a land devoid of stones to be used in the construction and without hard wood that would serve for this purpose, they only could count on the materials provided by nature, and these were the mud and reeds. But thanks to immigrants from the delta; who have brought with them knowledge of the realization of raw clay bricks it was possible that those were used in the construction of temples. They also used immensely high and rugged reeds and most of its buildings were carried out with these.
Dynasty of Sargon
Sumer was formed by several City-States, each of which was a political unit in itself with its own sovereign and laws; these City-States were unified by King Sargon I, in the year 2300 B.C. It is known by those scriptures that they had slaves and that the monarchy was dynastic, the Kings and dynasties mentioned in the Sumerian Kings list can be traced back in the middle of the third millennium.
In Sumer, most of its inhabitants in this historical period were already talking Sumerian language that is not related to other ancient languages that are known. Each city had a protector God with their corresponding temples, storages and houses and its inhabitants attended the religious function and management their large agricultural properties; while others were specializing in different trades such as weavers, potters and goldsmiths.
The dynasty of Sargon between (2300 – 2223 BC) has left few samples in monuments. Highly sophisticated cylindrical clay seals were used to mark documents or property, they are so numerous and informative that they constitute a key element understanding the many factor about this culture in general.
Cylinder seals of the SARGON period presented a change in the topics they represent. The ritual feast scene preferred in the early dynastic period is lost completely and are introduced a whole series of religious scenes and mythological themes represented in a rather dramatic way.
There is also a change in style. They moves from a crowded representation of the elements of the composition in the scenes; to be these free and independent figures gaining themselves a lot more importance within the entire “Assembly”.
Some sculptures have been found in the Temple of ABU, Tell Asmar, dating from a period approximately between the (2700 and 2600) they are a good statement about the sculpture of this Sargon period.
Most have overlapping hands on each other and crossed over the chest in reverential position, while the main figures represented by its high headdresses, have reptiles forms rather than human, a quality that is perhaps due to lack of skill of the artist, although this claim has not been proven, so also may have been intentional and with a meaning to represent accurately as possible the reality around them, since other figures representing animals are very well depicted with success.
Many of them are nude male statues in static position from the waist upwards carrying what looks like a skirt of woven wool. Men are show wearing long hair with a beard of wavy hair. The female figures were a kind of headgear. Sometimes the hair of these female figures is covered with a kind of cloth of linen; with which holding the hair. It is worth highlighting the fact about the hierarchical representation of the size of the figures; they are in order of importance from the gods to the worshipers. This custom is displayed both in the early period and in the subsequent periods as well, keeping as a constant in the Sumerian art and passing it along to other cultures with which they had contact. This formula have passed the test of times.

Have been found some sculptures in metal and also others made with the process that is known as the “Lost wax” as well as made of diorite, copper, gold and silver in warehouses, in which was kept not only grain, figs, etc., but also vessels, weapons, tablets of ceramics with detailed records of businesses, sculptures and possible anything related to the use and the administration of the Palace and the temple.
There are some figures showing a ritual nudity who have been also found and belong to this culture but; in a rather limited quantity representing figures of priests.
Was in Sumer where writing was developed for the first time, progressing from a stage of proto-writing prior up to the actual writing in the third millennium. However this literary awakening most of the population was illiterate, only scribes knew and developed this ability as it was the case in the majority of ancient cultures. It is not yet determined from where came the sumerian language as is not yet determined ether where the writing abilities come from.
Printed cuneiform tablets of pottery and cylinders has been of priceless value to know and understand many aspects of its social, administrative, political and religious system some of the parameters governing then displays a curious similarity to those governing today throughout the world.

Reliefs carved in stone ware apparently a popular artistic expression that enabled them to capture important events, legends, celebrations and of course respect for the gods as well as passages from their hostilities. The picture below show some genies from the Sargon II period.

Sumerian architecture seems to have developed two types of temples:
– Varied platform.
– Built at floor level.
The temples were; a kind of house of mud brick to which the gods supposedly; as the Sumerian disclaim, came to visit regularly, those homes were on platforms made of mud bricks also and were growing in size and height according to the course of the years. These platforms are known with the name of “Ziggurat”, and can be considered as one of the first large architectural structures.

In the Ubaid period (5200-c.3500 BC); the temple satisfied the formula with the majority of the architectural characteristics of the typical Temple of Sumerian platform. It is built of mud bricks on a raised plinth made of the same material, and its walls presented in its outer surface elements that fuse decorative look and structural reinforcement at the same time alternating between buttresses (brackets) and gaps on.
In both types of temples mentioned above decorative elements are made quite well and in which the appearance of the finish is carefully maintained. That is also the case of walls in the decor in which they used a mosaic artwork attached by cones of terracotta and sunk into the wall, its exposed ends look bright colors or they are coated in bronze.
UR Dynasty
The city of Lagash was a city of great importance in the Sumerian period and approximately in the 4th millennium BC still retained that preponderance and was a centre of artistic development under the supremacy of the Kings of “Ur”. It is known that during this period, this city had extensive commercial communications with distant realms. In this city the most important treasures of artistic value of the Sumerian culture have been discovered by archaeologists.

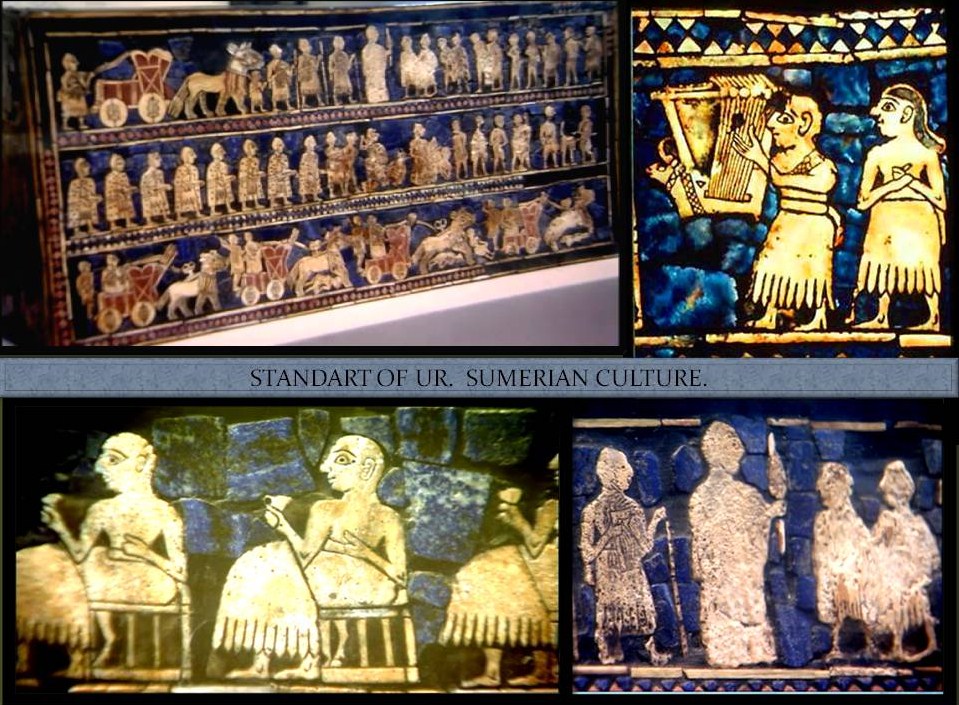
The sculpture representing a bull was used it with the purpose to decorate a harp
found in the tomb of Puabi date from around 2600 BC, exhibits a wealth of surprising decorative elements and is made of gold and lapis lazuli.
The standard of UR belonging to Sumerian Culture and from the UR dynasty is a very important art piece that shows the artistic skills rich by them in with the images represent different aspects in the life of these early civilizations. Some of them are rituals, ceremony, battles and the political and social division.
During the reign of Ur; the time in with some important developments contributed to the prosperity of the region, important events took place and modifications were made who elevated this civilization to a higher level.
- – Reforms were carried out: It was drafted the so-called code of “Ur-Nammu”.
- – They unified jurisprudence.
- – Established the equivalence between different currencies.
- – Existing channels were opened.
- – The temples were rebuilt.
- -In this period of splendor of the Sumerian arts were also made important sculptures with materials brought from far away as it is the case of the diorite; that have been found in excavations in this area.

Sumerian Art final conclusions
This culture has been known through their representations of art in different manifestations such as: architecture, sculpture and ceramics, these men had knowledge quite advanced for their time in many other subjects also as mathematics, chemistry, alchemy and medicine among other no less important as the astronomy and physics. How they come to such knowledge in a short amount of time remains still been an incognito.
These skills were enriched and evolving until amazing achievements were obtained during different periods by which the Sumerian culture crossed.
This claim could be verified thanks largely to the Scriptures, which were left in its buildings, sculptures, as well as different artifacts that were found in their warehouses. Some artifacts of funeral character were located in their buried sites and show not only functional value but also have a high artistic level.
In short, it can be said based on the important evidence found in these areas that Sumerian Ancient Culture was a solid foundation for many of the ones who also established later in this region, such as the Assyrians and the Babylonians.

Reliefs and exempt sculptures use religious themes and were also placed in these temples; not only as decoration element since they were also used as protection, devotion and adoration. It is considerable little what is known about the palaces and other buildings of the Sumerian culture.







