Rome in ancient times.
The Romans entered the Iberian Peninsula in 218 B.C. they started to create stable settlements from the middle of the 2nd century B.C The Romanization of numerous villages; either by wars or socio-cultural influence is propagated intensely and lasted more than five centuries. The Romans have left on its soil archaeological remains that have enabled study this interesting and rampant culture that had so much influence over the course of the history of mankind, laying the foundations of moral codes, justice, politics, religion, urbanization, and military strategy.
Rome was a people of farmers, merchants, warriors. The Romans showed greater interest in the practical things and their artistic works had always a utilitarian stamp. Dominated people, founders of a vast Empire, the Roman fundamental concern was to maintain dominance over the colonized territories, for which they mobilized powerful armies. The Roman empire gave life to a dense body of laws that tightened the relations between the metropolis and the provinces, and developed a gigantic constructive work with a varied repertoire of architectural forms perfectly adapted to its purpose of propaganda and funcionality. Their main merit is to have extended the Greco-Roman civilization for a vast part of the known world.
The Roman art develops from the Greek and Etruscan influences, reached its peak in the era of the Empire. Was held in Italy from the year 200 before C. until the 4th century after C. Some people had the opinion that Roman Art is inferior to the Greek art, but it was actually more varied, more flexible and in some aspects is closer to the modern art ; its influence in the art of the middle ages and the Renaissance was notable.
Romans painting
The roman’s paintings used new colors that were obtained from the combination of different substances as a base material, so the range is broader than the one used previously by the Greeks or even the Egyptians. Their painting show figurative features and innovative resources to develop them as faithful as possible to the reality, using elements such as mainstreaming, symmetry, the use of shadows to highlight the figures from the background and others with exquisite taste and mastery.
They used the technique of tempera color stains, applied with brushstrokes loose, without detail, as did centuries later the Impressionists with pretentious touches of shadow and light. Also in the painting is palpable a trend towards realism with some topics preferred such as the portrait, caricature and landscape.
Their works have a practical character used to decorate, but also had a strong propaganda elements to serve as support of the spreading of philosophy and Roman politics to the peoples with whom they had contact. In Roman Mural painting the fresco was the preferred method; although it has been pointed out that they must have used other techniques and even combine them.
From the 1st century, there are two pictorial trends or styles:
– The Neo attic style: they cares for the human form, highlighting issues of mythology and the epic.
– The Hellenistic style – Alexandrian: which shows concern for painting rural farming landscape and the sea.

In Roman painting there are four styles observed:
1. Inlay. (Imitates the decoration of marbles)
2. Architectural. (Imitates the lining and architecture)
3. Mixed or ornamental. (It is a mixture of the previous two)
4. Illusionist or staged. (Reloaded a mix of the second with the third style)
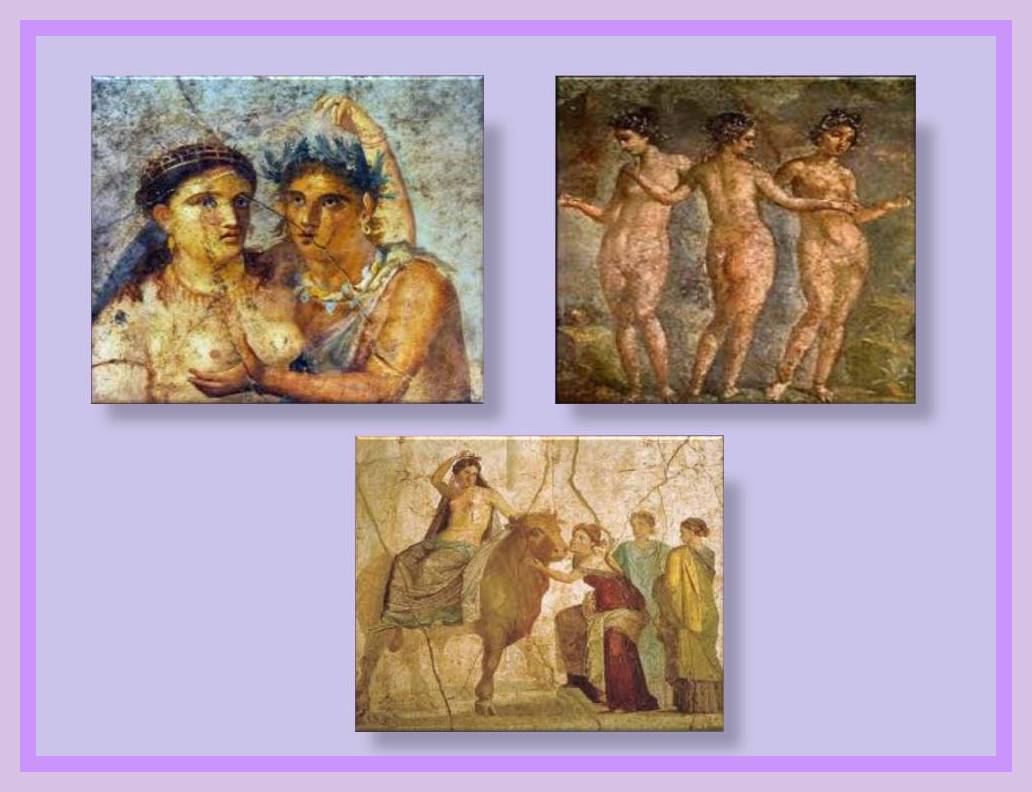
The erotic Roma’n painting with explicit sexual themes.
The philosophy of liberality allowed that the theme of the nude in both sexes could be expressed even with scenes quite explicit and daring where the figures appear occasionally in acts of sexual content, which can even today blush some. Paints with sexual content have been found more often in the walls of houses were sexual activities were perform as meaning of sexual services and also in the walls of the changing rooms at the public baths.
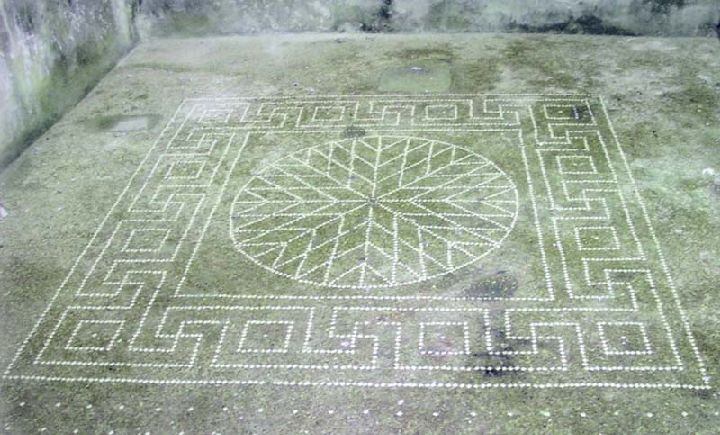
Roman Mosaic
Romans first start using the mosaic technique of decoration in walls and ceilings but later this complex technique was rather used more in the pavements. Magnificent paints decorations made from tesserae of marble, (an individual little tile, usually formed in the shape of a cube) depict a variety of themes using sometimes only two colors or in the case of the more complex one a rich polychrome.
Mosaic had wide representation in the palaces; they represent the same characteristics of the rest of Roman’s paint made in fresco or on other elements. Coming from Greek influences develop a more roman style were architectonic designs, geometrics or nature scenic decorations are elaborated resulting in works of expressive beauty were even precious metallic components like for example gold contribute to their splendor.
The Mosaic artist were very well recognized and well paid and the trade secrets of elaborations were mostly passing from families’ roots generation after generation. The flours in private villages, public buildings, the thermals rooms in public baths and the aristocratic palaces were all highly enriched with the mosaic decorations.
Themes more frecuently used in mosaic technique in Roma:
- Marine
- Death nature.
- Heroic legends
- Erotic themes
- Military Affairs
- The portrait
- Hunting topics
- Mythology
- Geometric
Roman Mosaic from the Old cathedral of Cartagena
Other roman painting techniques
Along with those other pictorial techniques used are the trestle; that were very popular among the upper classes of the Roman Empire and the small fresco painting. There was another technique well known as Encaustic made in fabric or wood. Many details of the Roman painting are Know through the frescoes found in the city of Pompeii, they are seen as is they are copies of Greek paintings; based on the themes they are showing and the techniques used.
The poverty of the architectural materials used in Roman buildings enabling a development of mural painting. The use of materials such as concrete, brick or masonry, were forced to put a coating on them. So walls were treated with a layer of white and fine stucco which later were polish. The stucco was marble reduced to powder mixed with lime or cola to apply them to the wall.
Two names stand out as precursors artist of Roman history painting:
– Fabius: Painter hardly known, lived around 300 BC.
– Painter Pacuvius of which we know nothing of his artistic production although we imagine that his tendency towards the Greek would be decisive.
These two painters tend to represent a kind of historical paintings in which depictions of battles and the commemorations of WINS would be the most frequent topics. These military scenes were conceived as propaganda posters that exhibited the winners Generals in their triumphal walks to return home.
The Roman technique of produce murals inside the houses was inspired by the Greek, with if refers as the wall dividing into three parts:
– The base foundation.
– Superstructure
– Intermediate zone.
Another innovation of Roman painting is the opening of the wall through a painted perspective in the form of open window in which introduced the characters in two ways:
– Through small figurative paintings
– By placing the characters in the baseboards as a theatrical space.
The absence of furniture and large patios and room’s made necessary those coatings. The painting that has come down to us is not representative of the Roman era; the painters in this era were craftsmen with rather special abilities and knowledge about techniques and Greek themes.
The colors were applied to the wall newly plastered and wet, with this made that these colored inks penetrated, creating a thick layer. Sometimes they painted directly if the plaster had dried. This painting is immediately recognized because of it little adhesion of the color who produced then to crack more easily.
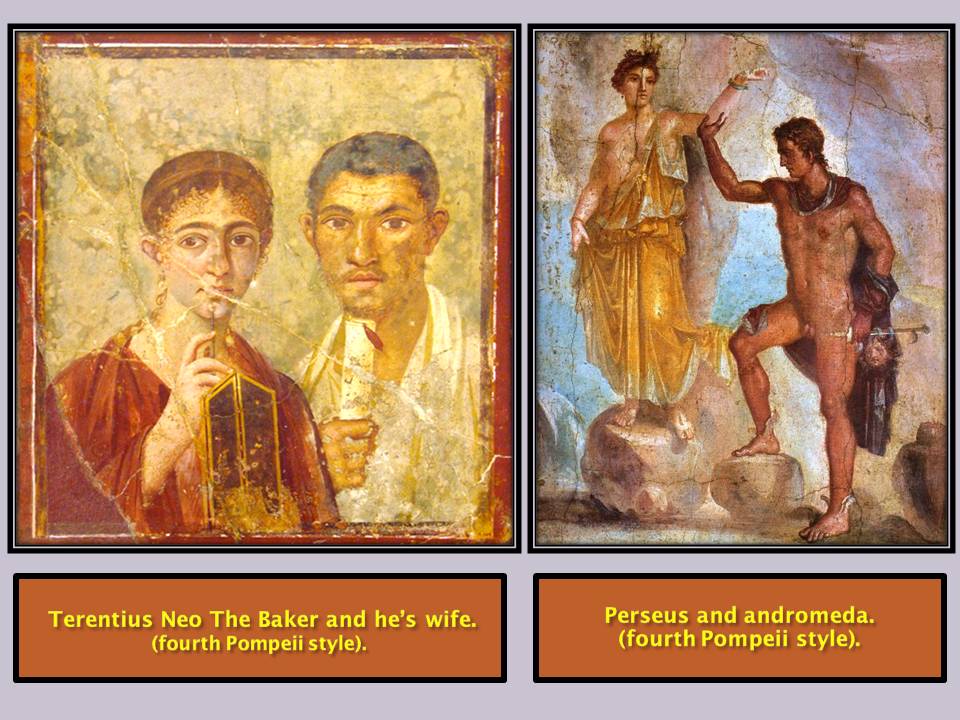
The Stylistic and chronological division of Roman painting in Pompeii.
- Early Pompeian style
- Second Pompeian style
- Third Pompeian style
- Fourth Pompeian style.
The earthquake and Volcanic eruption happened in the city of Pompeii in year 63 caused such damage that most of the city had to be rebuild. Therefore all coatings were made again, despite the fact that some years later they were damaged in the eruption of Vesuvius. The technique used in these new paintings sought the unreal effects leaving aside the expertise and previous amazing refinement. Architectural simulations are replaced with fantastic painted compositions; they are not referred to an objective reality.
The examples that have reached us, both Rome and Pompeii, make that we can differentiate between the two geographical areas.
– In Pompeii there is a predilection for bright purple, red cinnabar, the deep blue colors, or the golden yellow for the columns.
– However in Rome, the intonations are clear on totally white backgrounds.