Roman architecture
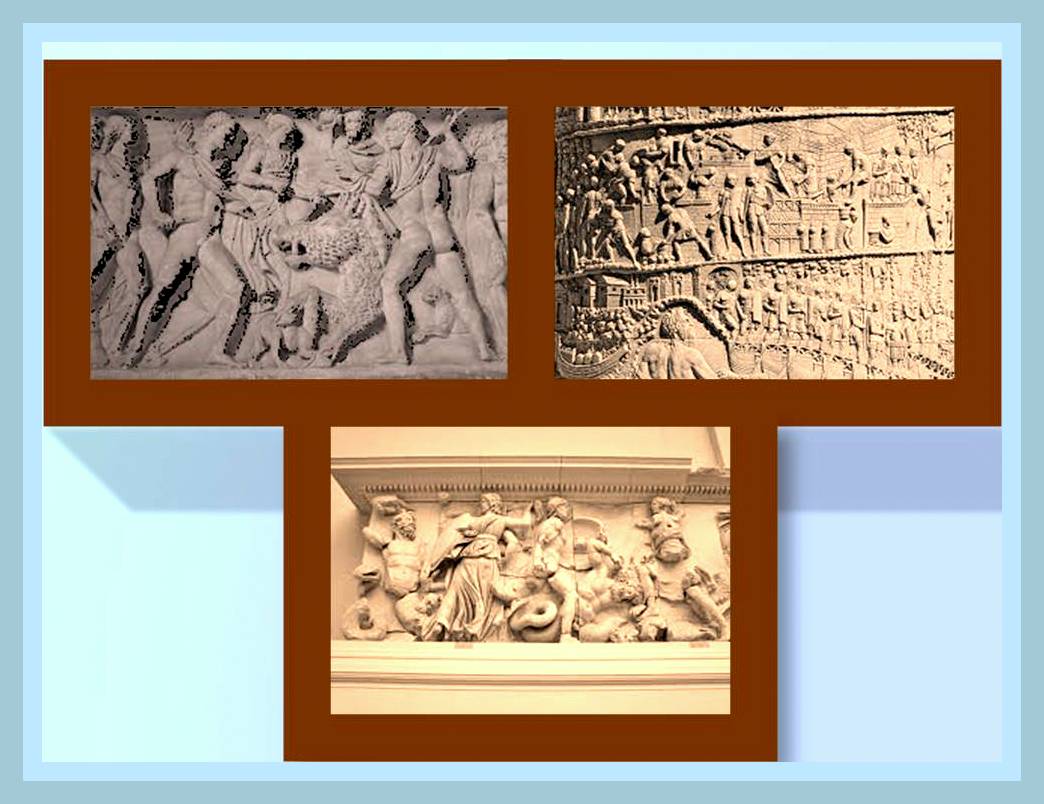
The development reached in the Roman architecture was so important that even the drawing and painting are made to service the architecture. The sculpture were also very important part in the buildings, supporting their political and religious propaganda.
They all come together helping to support the functional and practical character of Roman culture. With the propaganda element implemented as main characteristic, they generalizes and unify their aesthetic and technical concepts, extending them to the entire region in which the Romans establish their culture.
The sculptures and relieves applied to the buildings are important parts in the propagandistic roman aestheticists concept (as mentioned before), they provided examples and guides to be followed by the citizens in different aspects like: clothing, philosophical thinking as well as political tendencies.
The emphasis in spread the messages to the spectators through the artistic elements located in the buildings as decoration, have contributed to a better knowledge today about this culture in relation to religion, politics and philosophical aspect, providing an insight in their everyday life aspects as well.
The architecture in Rome is seen as a very centralized and unitary art; in which its constructive and aesthetic canons are extended to the entire empire and influences in the public and private lives of its citizens. Of course it is a monumental architecture which seeks to represent the majesty expressions of strength and power that represent the ideal of uniformity proper of the Empire.
It alternates between two known systems:
1 Of the column and copying lintel of the Greeks.
2. The arch and Vault which took from the Etruscans.
The employed vaults were mainly:
-The domed.
-That of barrel
-In oven
– Aristae
Roman’s main monuments were:
-The temple
-The Basilica
-The Thermae
-theatres
-the amphitheatres
-circuses
The materials used in Rome architecture were basically:
-The stone masonry
-The masonry
-The brick often combined with concrete mortar.
Awesome Roman engineering can be appreciate in this 3d virtual restoration comparing how looks today with how must have been looks like in ancient times.
Although the Romans employed the classical Greek architectural orders, they used more freely combining them together in the same facade; one older was used for the first floor another for the second and so on. They utilize others orders too like the Tuscan for example and this have in many case to do with the region were the building was constructed besides the functional characteristic of this one.
The Roman temple
a) Take of the Etruscan Temple its location on a high podium with a unique front access.
b) From the Greek temple takes the long cellar (also known as naos is the space or room internal located in the sanctuary of the temple where stood the statue of the God).
c) Also from Greek takes the Colonnade perimeter (edge outside of two dimensional figures), but except for the portico of access; in with they are removed, are attached to the wall.
d) It is in the front of the building where its appearance is more similar to the Greek world.
The Thermae
They were large architectural complexes of recreation and public health, in which were settled baths of different temperatures. The Thermae or baths played a key role in Roman social life, not only as a spa; but also as places of meeting and recreation, they could sometimes acquire extraordinary proportions accommodating thousands of people. They were equipped with library, restaurants, and gyms areas among other commodities.
Romans in ancient times use to take care of their bodies, as well as they did in relation to the intellectual aspect. And the concept of healthy mind in healthy body were also for them as it was for the Greek and important priority in their live.
They have free access for all the population and because of the scandals that had developed in the commune’s rooms for both sexes they were separated after these issues assigning areas for the ladies and other for the man’s.
Those for the man’s; have interesting painting over their assigned place to accommodate their clothes, with explicit sexual allusions themes, that could turn red some faces even today.

The Thermae count with:
-A room to undress or “apodyterium”
-Cold baths or “frigidarium”
-Temperate baths or “tepidarium”
-Hot baths or “caldarium”
-Fitness Center
-Massage zones
-Libraries and open spaces for a walk.
An example is the baths of Caracalla in Rome for up to a thousand people.
This video show a virtual 3d restauration of a Roman thermae.
Las termas de Caracalla. Impresionante reconstrucción 3D de Altair4.
Posted by Traianvs. Ingeniería Romana on Friday, March 25, 2016
The Basilica
Building of three naves separated by columns and topped in apse or cupola, was the place dedicated to commercial transactions and also served as a court.
In the Curia (Congregational space) were held political meetings and meetings of citizens and had a large rectangular room with one or two stances.
The main and widest nave, was supported by columns with space between them and the outer wall, with the purpose to serve as a gallery or corridor, facilitating the translation between the entrance and the back; when the halls were full of people. Difference of heights were used to open holes for lighting in the upper part of the walls. The basilicas were located in the Forum.
Following the fall of the Roman Empire and in Christian times these basilicas are used as a center of Congregation of the faithful, very similar in their use which are given to the churches.
Some of the most emblematic buildings of the Roman world were devoted to the shows. They used to be close to the city, but outside the walls. Among them we have:
The Roman Theatre
Were inherited from the Greeks, dedicated to the representation of works of classical playwrights, they were semicircular and divided in:
-Orchestra.
-Scenario.
-Aditus (aisles from entrance to the orchestra).
-Cavea. (Was the place where the spectators accommodated himself according to their social rank).
Although The Roman Theatre derives directly from Greek, there are some differences:
- The Roman Theatre is installed without take advantage of the decline of the ground, building on a completely domed structure of arches and vaults of brick or concrete.
- “The Cavea is installed with “scene”; stages of monumental proportions with sculptures and very decorated.
- The “orchestra” becomes semicircular rather than circular.
- Gardens and “Peristylus” were in the back.
The theatres were built with stone and Roman mortar as building materials, the same materials as well were used in other types of buildings such as;
- The amphitheatres.
- Circuses.
- Forums.
- Temples.
The aesthetics of the outside also had importance, presenting a series of floors. In those play an important role the arch and column. In the intermediate vain mediate statues were placed. Many theatres had small temples in its structure. Viewers weren’t given harsh time really to wash the show, because climate construction elements in this buildings were installed awning to protect them from the rain or the light of the Sun.
Amphitheatre
Space oval fruit of the Union of two theatres for the scene (hence its name) was used as a site for the contemplation of struggles of animals, Gladiators, circus exercises, simulation of naval battles, etc.
The aqueducts
Those was one the most spectacular exponents of Roman architecture and their incredible clever engineering knowledge. Those bridges carried water to the cities from springs or rivers. Its construction was very complex and sometimes they had to save large uneven areas so in those, was done its structure of arches; (corridor or open spaces in arched galleries) these were overlapping.
The circus
It was destined to “Cuádriga” racing and was a very elongated space in the Center was placed the spine with large statues. The Roman circuses had a leading role in social life; many people conglomerate in those places and they were built large and confident, ready to host them during the representation.
The Roman Coliseum is the largest of these buildings dedicated to games and entertainment for the masses.
Unlike the first amphitheaters, whose location sought to be in hills to provide support to the walls, the Coliseums is an outstanding building constructed using stone and cement, 48 meters high and 188 long and 156 m wide with capacity for 50,000 spectators who could access or get out of there in less than three minutes thanks to a complex network of passages and exits.
These buildings were done primarily with constructive elements oriented to make pleasant the experience of the conglomerates to watch the show, easy to scroll galleries and corridors, visibility from the stands etc.
The constructive elements consisted basically in:
- “Porta “Pompeii (without stands, visitor’s entrance)
- “Carceres” (post output, slightly inclined to distance adjustment)
- “Pul vinar” (presidential Parco)
- “Triumphal Porta” (semicircular tiers where were the judges.)
The arch of triumphs; for with the Roman soldiers pass in and out of the city are a maximum representation of the power and domination concept needed for them to be spread around not only to their citizens but to the entire region under Roman subordination.
The cities were major center of coexistence and in general the Roman civilization needed to defend itself against aggression.
Roman cities were created on indigenous settlements or newly created, demanded the construction of great works to save rivers, provide safe drinking water to the city or facilitate trips between those cities. Therefore, some of the most interesting works of Roman architecture were bridges, aqueducts and roads.
The cities in with thousand of hundreds of people live in an urban, practical and very down to earth society; had a construction system with very clever fixtures to provide the citizens with civil, religious and official buildings as well. They also constructed buildings dedicated to business and recreational porpoises. Often these buildings were situated in the Forum, real neuralgic Center of the Roman city.
The ruins of Pompeii provided and invaluable archeological and historical resources on how these cities must had been looks like.

There is a post about the Roman relief sculpture that is also very important to understand their architecture. Is at this link: