The Egyptian art
Their thoughts and cosmological view of the world, their economic activities and of course their religion; form a single whole closely related that must be study and understand in order to get a clearer idea of the General characteristics of the Egyptian art.
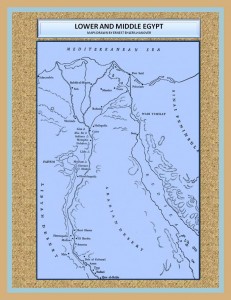
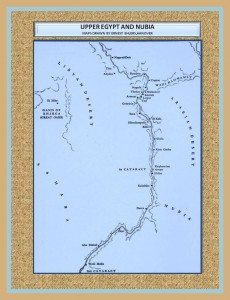
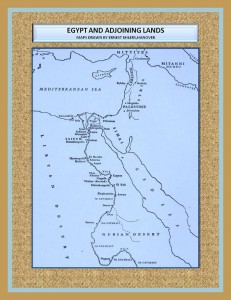
The Nile River is the heart of the Egyptian land, hear was founded this civilization which depends on its flow for their own subsistence. The benefits offered by the River allowed the development and flowering of this interesting people and culture.
It is not surprising that because of the need to adaptation to the harsh climatic conditions of the desert they look to the River as a miraculous giver of life; as palliative and Solver of the challenge of survival in this adverse environment. Their settlements close to the Nile enable them to develop an agrarian economy by taking advantage of flooding from the River; in the black soil or Kemet formed after retiring this waters. This sediment was rich in nutrients for crops.
These three stations were:
I. Akhet: Flood (June-September)
II. Peret: (October-February) of crops grown.
III. Shemu: (March–June) collection of crops.
Based on the type of agricultural economy; which depends largely on the nature they develop skills such as geometry, wide application of mathematical measures, the development of architecture in homers levels and a curious sense of decoration which does not overlook the very nature as inspiration.
The Egyptians had a very orderly and serene view of the world; it is as if they look the events of life through a filter or sieve where everything at the end of this fit with his cyclical view of life. It was their belief that by perfect was the life on earth; does not end after the death but continued beyond then and need to be ensure the body, mind and well-being so they transcend on the trip save; to that other place where can be returned resurrected”.
Like the Nile had cyclical floods, for the Egyptians life was also in constant renewal. For them their gods live, die and resurrect constantly.
 It is as if the life laid out for them as a terrestrial statism, in which nothing changes; even after death, for them the death is not more than a stage on the way to the resurrection.
It is as if the life laid out for them as a terrestrial statism, in which nothing changes; even after death, for them the death is not more than a stage on the way to the resurrection.
There is no need to say that this way of seeing the world establish a strong conservatism and this is based (not in the fear of change itself); but in the start of what for them is already perfect and there is no need for change anything; it just have to be keep it like this; as the gods created.
For a long time in their history man is not in possession of Knowles of distinction between his personal being and the word around him. He does not distinguish between earthly and supernatural phenomena yet.
The grade of men consciousness related to his part in the word surrender him; gained territory in people minds far further in the Neolithic period and evolve progressively for many culture; but for the Egyptians as in no other country men’s deed and thoughts were governed by the concern for the after-life and this believes where way to affianced in this culture for a consider high amount of time to be abandoned ease, even when they were at times under others culture domination.
Their geographical position contributes even more to the isolation and lack of evolution in those believes.
The Supreme maintainer for them that this perfect State could be keep was the Pharaoh, that first figure in which are represented religion and State simultaneously and more revered it; It was who was blamed if the State of perfection, serenity and balance not go as expected.
The geographical position of Egypt kept it fairly isolated from other peoples and their cultural influences for a long time. The isolation accentuated their concept of life and its proud vision in relation to the world.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EGYPTIAN ART:
- Art created with destination to the Church who was in Egypt a single whole.
- The artist is more a craftsman, completely anonymous running norms and pre-established concepts.
- The accuracy of execution of orders is what is appreciate; not the originality of the craftsman.
- Art is the propagandistic support of the power of the State – religion.
- The image carries a symbolism and a message; it is not with the intention of showing beauty to be referred to as aesthetic pleasure.
- They relinquish the prospect to give greater clarity and emphasis to the message.
- The proportions and resulting strokes in the figure are optically incoherent in function to transmit; melted in the resulting message the conceptual elements of propaganda.
- The figures show position of frontality; is a fixed concept which is repeated.
- The figures are made solid to ensure sustainability.
- Pure geometric lines such as the one in architecture forms are used.
- Animals and plants are widely represented both in painting and ceramics.
The Egyptians made their works of art to always stick to the religious character and serving propaganda after this religiosity which guaranteed control over crowds and made possible the absolute supremacy of the power in the figure of the Pharaoh. They of course aroused the funerary aspect as the main symbol responding to their concept of philosophy of life.
Despite being over time these tombs funeral homes and other monuments staled and devastated have reached us objects in very good condition and they are consider today important works of art despite having been made by anonymous craftsmen as mere execution of orders.
These objects have provided invaluable information on this enigmatic culture. While they not always address in the representation of their scenes facts of daily life such as the Sumerians did, their stories, historical periods and philosophical concepts have not gone unnoticed for the history of art which has organized this culture with more than 3000 years of evolution in divisions of their periods in order to understand it better.
1 · Tinita time: 3000-2778 Egyptian capital.
2 · Ancient Empire: 2778 to 2263 with capital at Memphis.
3 · First intermediate period: 2263 until 2160.
4 · Median Empire: 2160 – 1785 with its capital at Thebes.
5 · Second intermediate period: from 1785 until 1580.
6 · New Empire: 1580 to 1085: with the capital in Thebes.
7 · Low time: 1085-333: Persian domination of Egypt.
8 · Coptic Era: The domain of Egypt under the Greek and the Roman.